AWS Data Pipeline Components
| Category | Use cases | Service | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Analytics | Interactive analytics | Athena | Athena is an interactive query service that makes it easy to analyze data in S3 using standard SQL. |
| Big data processing | EMR | EMR is the industry-leading cloud big data platform for processing vast amounts of data using open source tools such as Apache Spark, Hive, HBase,Flink, Hudi, & Presto. EMR | |
| Data warehousing | Redshift | The most popular & fastest cloud data warehouse. | |
| Real-time analytics | Kinesis | Kinesis makes it easy to collect, process, & analyze real-time, streaming data so one can get timely insights. | |
| Operational analytics | Elasticsearch Service | Elasticsearch Service is a fully managed service that makes it easy to deploy, secure, & run Elasticsearch cost effectively at scale. | |
| Dashboards & visualizations | Quicksight | QuickSight is a fast, cloud-powered business intelligence service that makes it easy to deliver insights to everyone in organization. | |
| Data movement | Real-time data movement | 1) Amazon Managed Streaming for Apache Kafka (MSK) 2) Kinesis Data Streams 3) Kinesis Data Firehose 4) Kinesis Data Analytics 5) Kinesis Video Streams 6) Glue | MSK is a fully managed service that makes it easy to build & run applications that use Apache Kafka to process streaming data. |
| Data lake | Object storage | 1) S3 2) Lake Formation | Lake Formation is a service that makes it easy to set up a secure data lake in days. A data lake is a centralized, curated, & secured repository that stores all data, both in its original form & prepared for analysis. S3 LakeFormation |
| Backup & archive | 1) S3 Glacier 2) Backup | S3 Glacier & S3 Glacier Deep Archive are a secure, durable, & extremely low-cost S3 cloud storage classes for data archiving & long-term backup. | |
| Data catalog | 1) Glue 2)) Lake Formation | ||
| Third-party data | Data Exchange | Data Exchange makes it easy to find, subscribe to, & use third-party data in the cloud. | |
| Predictive analytics && machine learning | Frameworks & interfaces | Deep Learning AMIs | Deep Learning AMIs provide machine learning practitioners & researchers with the infrastructure & tools to accelerate deep learning in the cloud, at any scale. |
| Platform services | SageMaker | SageMaker is a fully managed service that provides every developer & data scientist with the ability to build, train, & deploy machine learning (ML) models quickly. |
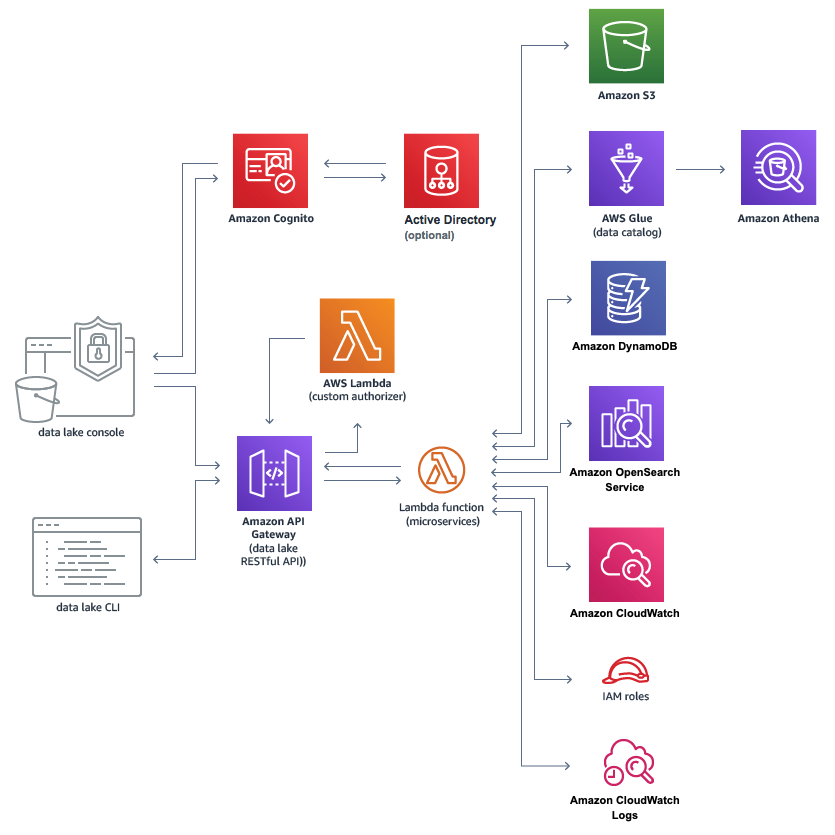
Data Lake on AWS
The code configures a suite of:
- AWS Lambda microservices (functions)
- Amazon OpenSearch Service for robust search capabilities
- Amazon Cognito for user authentication
- AWS Glue for data transformation
- Amazon Athena for analysis
- Amazon S3 using security, durability, and scalability to manage a persistent catalog of organizational datasets
- Amazon DynamoDB to manage corresponding metadata. Once a dataset is cataloged, its attributes and descriptive tags are available to search on. - Athena Users can search and browse available datasets in the console, and create a list of data they require access to. It keeps track of the datasets a user selects and generates a manifest file with secure access links to the desired content when the user checks out.
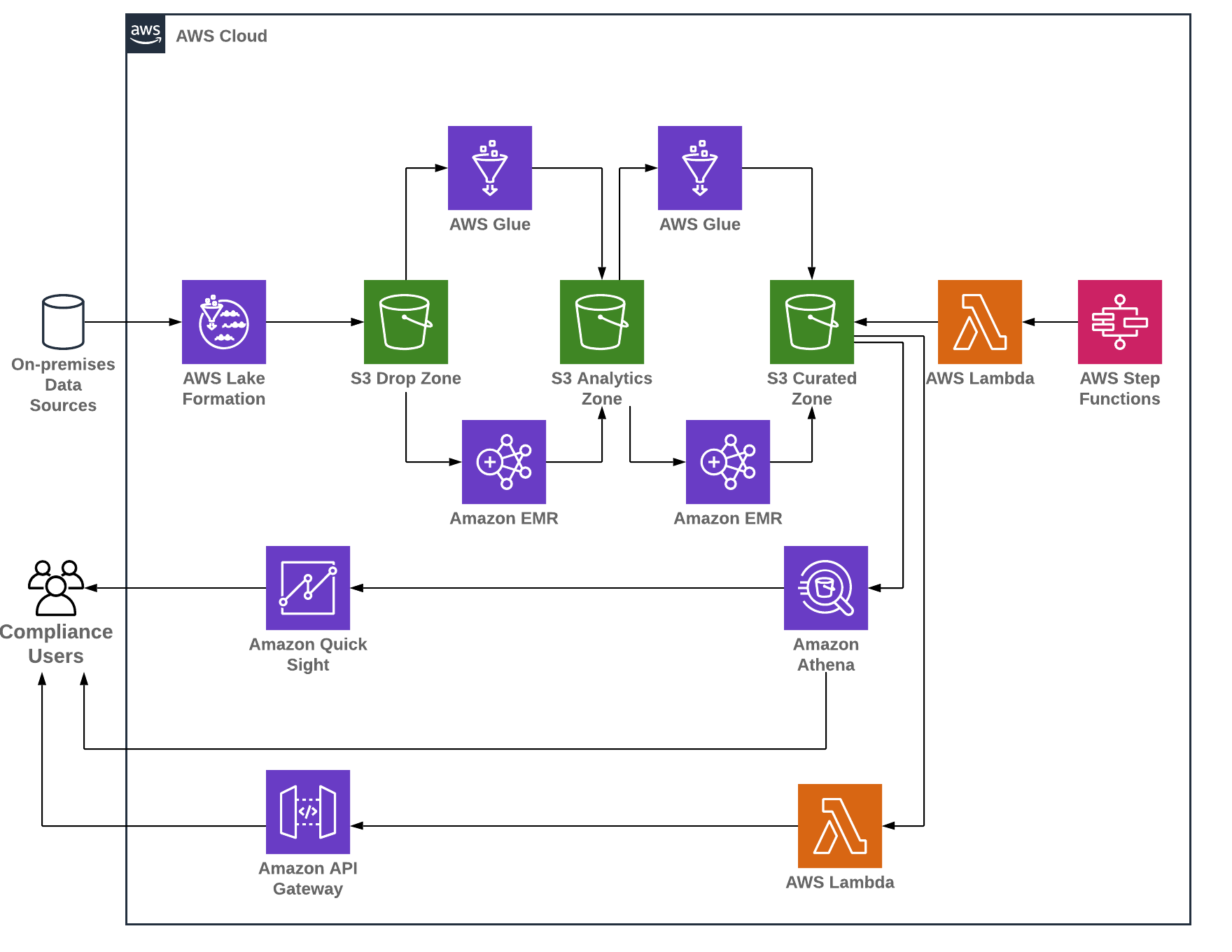
Lake Formation on AWS
- User personas: As first step, the DMO team identified three user personas for the Audit Surveillance system on AWS.
- Data service compliance users who would like to consume audit surveillance data from the data lake into their respective applications through an enterprise data service.
- Business users who would like to create business intelligence dashboards using a BI tool to audit data for compliance needs.
- Compliance IT users who would like to perform ad-hoc queries on the data lake to perform analytics using an interactive query tool.
- Data ingestion: Data is ingested into Amazon Simple Storage Service (S3) from different on-premises data sources by using AWS Lake Formation blueprints. AWS Lake Formation provides workflows that define the data source and schedule to import data into the data lake. It is a container for AWS Glue crawlers, jobs, and triggers that are used to orchestrate the process to load and update the data lake.
- Data storage: Parametric used Amazon S3 as a data storage to build an Audit Surveillance data lake, as it has unmatched 11 nines of durability and 99.99% availability. The existing Hadoop storage was replaced with Amazon S3. The DMO team created a drop zone (raw), an analytics zone (transformed), and curated (enriched) storage layers for their data lake on AWS.
- Data cataloging: AWS Glue Data Catalog was the central catalog used to store and manage metadata for all datasets hosted in the Audit Surveillance data lake. The existing Hadoop metadata store was replaced with AWS Glue Data Catalog. AWS services such as AWS Glue, Amazon EMR, and Amazon Athena, natively integrate with AWS Glue Data Catalog.
- Data processing: Amazon EMR and AWS Glue process the raw data and places it into analytics zones (transformed) and curated zones (enriched) S3 buckets. Amazon EMR was used for big data processing and AWS Glue for standard ETL processes. AWS Lambda and AWS Step Functions were used to initiate monitoring and ETL processes.
- Data consumption: After Audit Surveillance data was transformed and enriched, the data was consumed by various personas within the firm as follows:
- AWS Lambda and Amazon API Gateway were used to support consumption for data service compliance users.
- Amazon QuickSight was used to create business intelligence dashboards for compliance business users.
- Amazon Athena was used to query transformed and enriched data for compliance IT users.
- Security: AWS Key Management Service (KMS) customer managed keys were used for encryption at rest, and TLS for encryption at transition. Access to the encryption keys is controlled using AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) and is monitored through detailed audit trails in AWS CloudTrail. Amazon CloudWatch was used for monitoring, and thresholds were created to determine when to send alerts.
- Governance: AWS IAM roles were attached to compliance users that permitted the administrator to grant access. This was only given to approved users or programs that went through authentication and authorization through AWS SSO. Access is logged and permissions can be granted or denied by the administrator. AWS Lake Formation is used for fine-grained access controls to grant/revoke permissions at the database, table, or column-level access.
Kinesis on AWS
- Problem Statement
- To design and implement a fully temporal transactional data lake with the repeatable read isolation level for queries is a challenge, particularly with burst events that need the overall architecture to scale accordingly. The data store in the overall architecture needs to record the value history of data at different times, which is especially important for financial data. Financial data can include corporate actions, annual or quarterly reports, or fixed-income securities, like bonds that have variable rates. It’s crucial to be able to correct data inaccuracies during the reporting period.
- The example customer seeks a data processing platform architecture to dynamically scale based on the workloads with a capacity of processing 150 million records under 5 minutes. Their platform should be capable of meeting the end-to-end SLA of 15 minutes, from ingestion to reporting, with lowest total cost of ownership. Additionally, managing bi-temporal data requires a database that has critical features, such as ACID (atomicity, consistency, isolation, durability) compliance, time-travel capability, full-schema evolution, partition layout and evolution, rollback to prior versions, and SQL-like query experience.
- Solution overview
- The solution architecture key building blocks are Amazon Kinesis Data Streams for streaming data, Amazon Kinesis Data Analytics with Apache Flink as processing engine, Flink’s RocksDB for state management, and Apache Iceberg on Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3) as the storage engine (Figure 1).
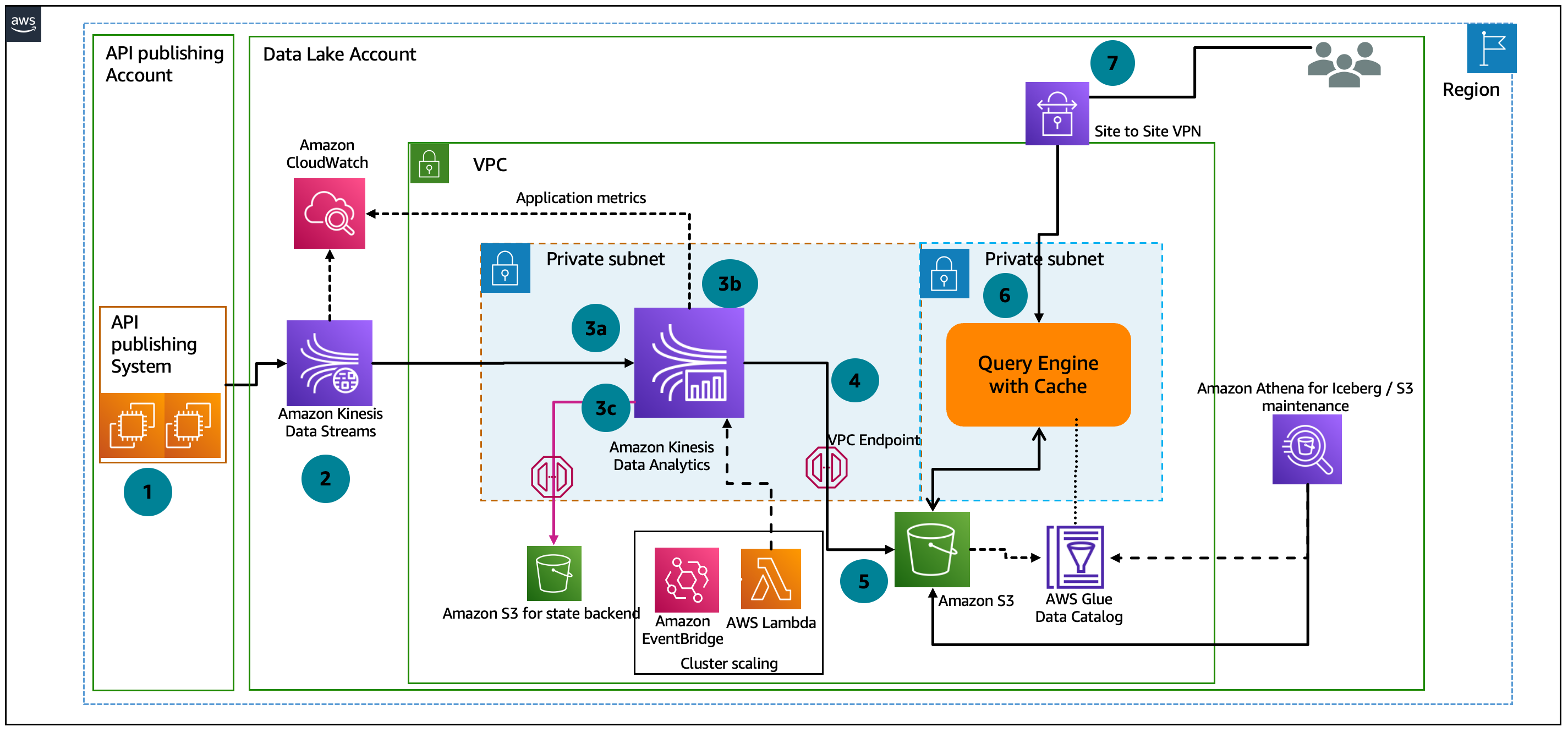
- Data processing Here’s how it works:
- A publisher application receives the data from the source systems and publishes data into Kinesis Data Streams using a well-defined JSON format structure.
- Kinesis Data Streams holds the data for a duration that is configurable so data is not lost and can auto scale based on the data volume ingested.
- Kinesis Data Analytics runs an Apache Flink application, with state management (RocksDB), to handle bi-temporal calculations. The Apache Flink application consumes data from Kinesis Data Streams and performs the following computations:
- Transforms the JSON stream into a row-type record, compatible with a SQL table-like structure, resolving nesting and parent–child relationships present within the stream
- Checks whether the record has already an existing state in in-memory RocksDB or disk attached to Kinesis Data Analytics computational node to avoid read latency from the database, which is critical for meeting the performance requirements
- Performs bi-temporal calculations and creates the resultant records in an in-memory data structure before invoking the Apache Iceberg sink operator
- The Apache Flink application sink operator appends the temporal states, expressed as records into existing Apache Iceberg data store. This will comply with key principles of time series data, which is immutable, and the ability to time-travel along with ACID compliance, schema evolution, and partition evolution
- Kinesis Data Analytics is resilient and provides a no-data-loss capability, with features like periodic checkpoints and savepoints. They are used to store the state management in a secure Amazon S3 location that can be accessed outside of Kinesis Data Analytics. This savepoints mechanism can be used to programmatically to scale the cluster size based on the workloads using time-driven scheduling and AWS Lambda functions. If the time-to-live feature of RocksDB is implemented, old records are stored in Apache Iceberg on Amazon S3. When performing temporal calculations, if the state is not found in memory, data is read from Apache Iceberg into RocksDB and the processing is completed. However, this step is optional and can be circumvented if the Kinesis Data Analytics cluster is initialized with right number of Kinesis processing units to hold the historical information, as per requirements.
- Because the data is stored in an Apache Iceberg table format in Amazon S3, data is queried using Trino, which supports Apache Iceberg table format.
- The end user queries data using any SQL tool that supports the Trino query engine.
- Apache Iceberg maintenance jobs, such as data compaction, expire snapshot, delete orphan files, can be launched using Amazon Athena to optimize performance out of Apache Iceberg data store. Details of each processing step performed in Apache Flink application are captured using Amazon CloudWatch, which logs all the events.
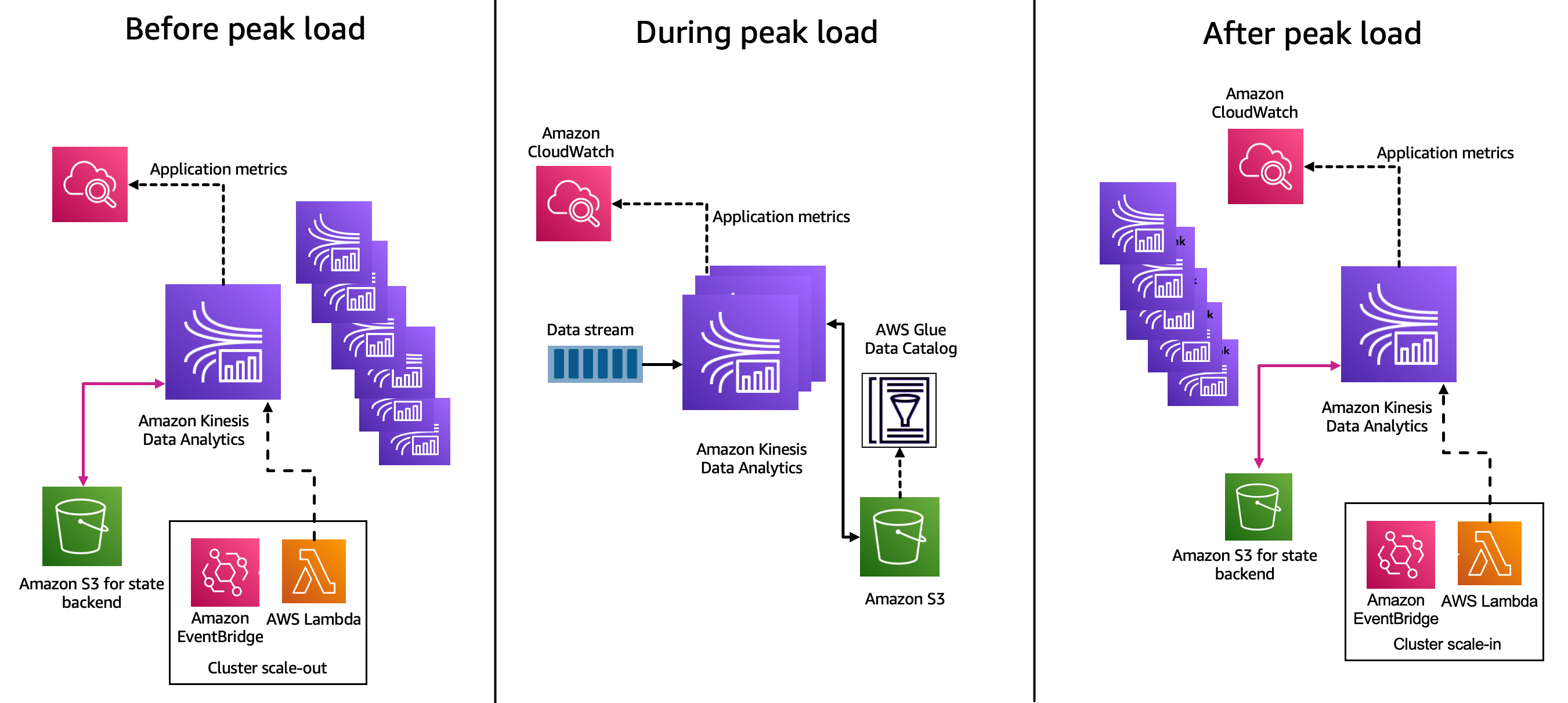
- Scalability
Amazon EventBridge scheduler invokes a Lambda function to scale the Kinesis Data Analytics. Kinesis Data Analytics has a short outage during rescaling that is proportional to the amount of data stored in RocksDB, which is why a state management strategy is necessary for the proper operation of the system.
Figure 2 shows the scaling process, which depicts:
- Before peak load: The Kinesis Data Analytics cluster is processing off-peak records with minimum configuration before the peak load. A scheduled event is launched from EventBridge that invokes a Lambda function, which shuts down the cluster using the savepoint mechanism and scales up the Kinesis Data Analytics cluster to required Kinesis processing units.
- During peak load: When the peak data burst happens, the Kinesis Data Analytics cluster is ready to handle the volume of data from Kinesis Data Stream, and processes it within the SLA of 5 minutes.
- After peak load: A scheduled event from EventBridge invokes a Lambda function to scale down the Kinesis Data Analytics cluster to the minimum configuration that holds the required state for the entire volume of records.
–